Data Structure – Grasshopper
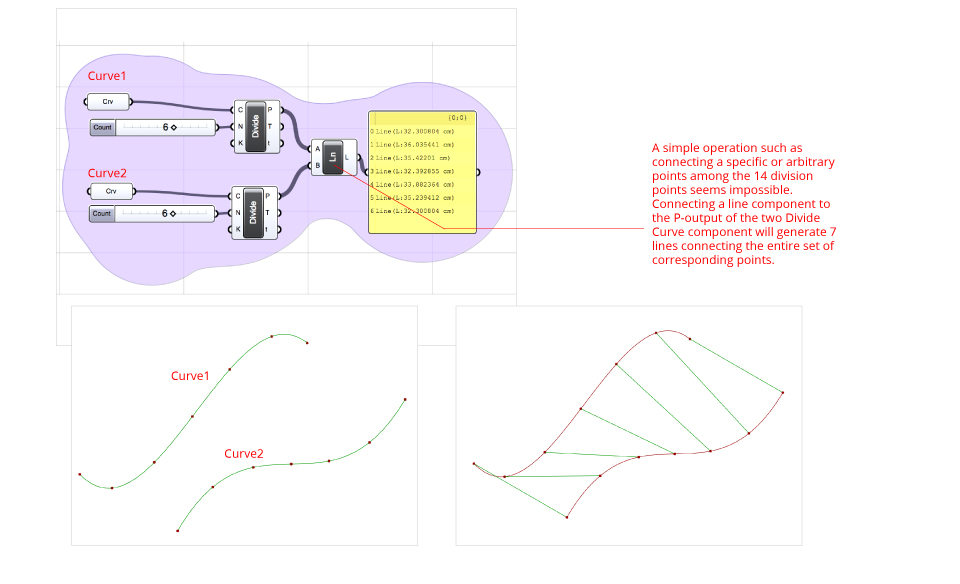
Filters – One of the effects of the lack of “physical” interaction in grasshopper is the seemingly difficulty in selecting items among a set of objects. In this example two curves are drawn and assigned to two different “curve” components curve1 and curve2 and then divided into 6 parts using the divide component and a slider. As a result, seven parts are generated on each curve. A simple operation such as connecting a specific or arbitrary points among the 14 division points seems impossible. Connecting a line component to the P-output of the two Divide Curve component will generate 7 lines connecting the entire set of corresponding points.
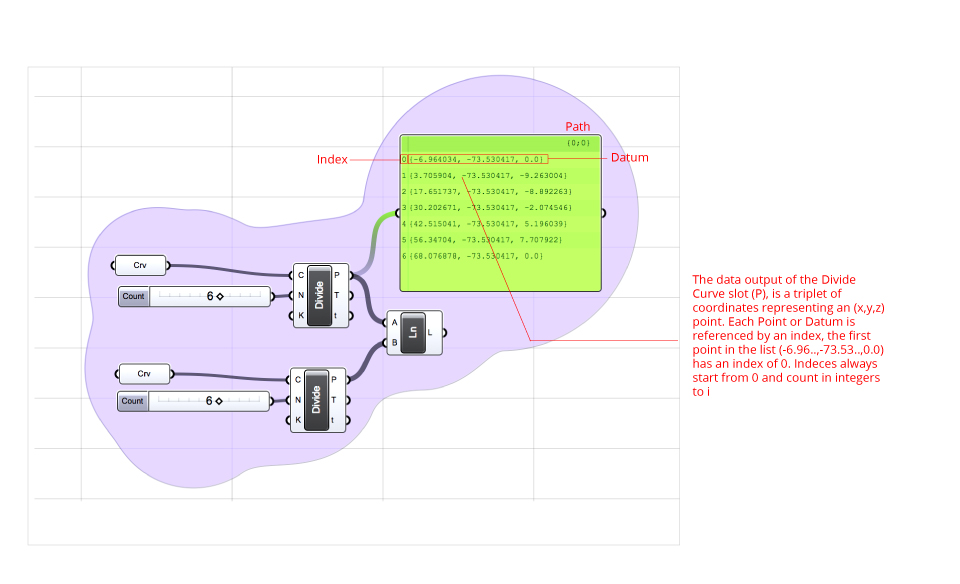
Grasshopper structures data into paths, hierarchical levels that contains data list (arrays). These are further subdivided into items which are index (0 to i) to reference an item’s position
List Item – Select a specific item form a list. Understanding a lists allows us to select a specific datum within a List by referring to its index by a filter.
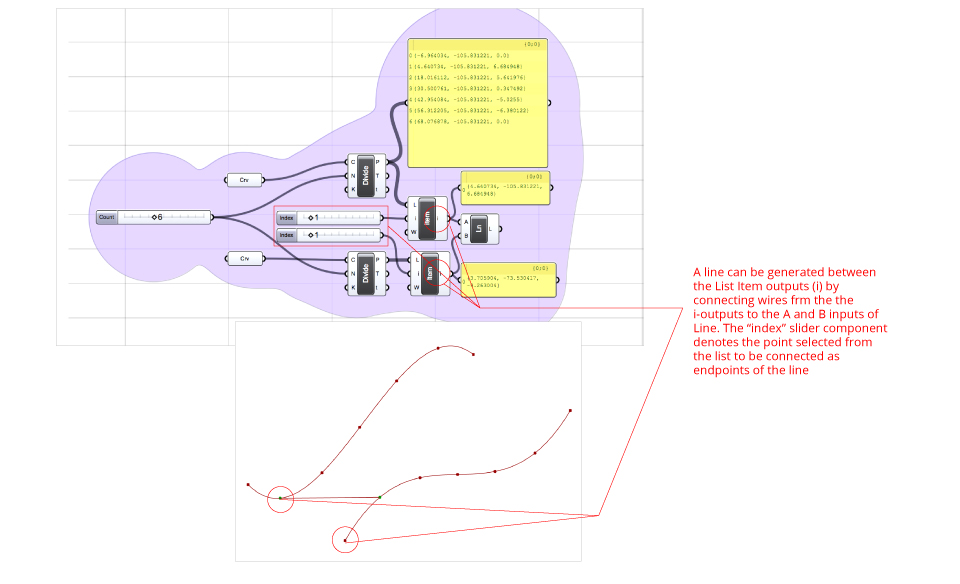
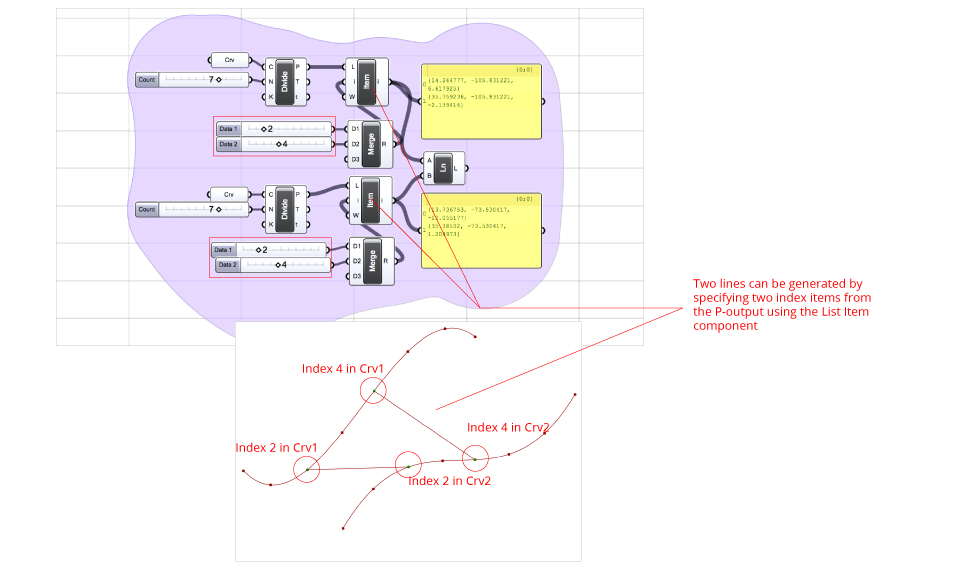
In order to select two or more items, several sliders can be connected to the i-input of the component List Item, by using the Merge component
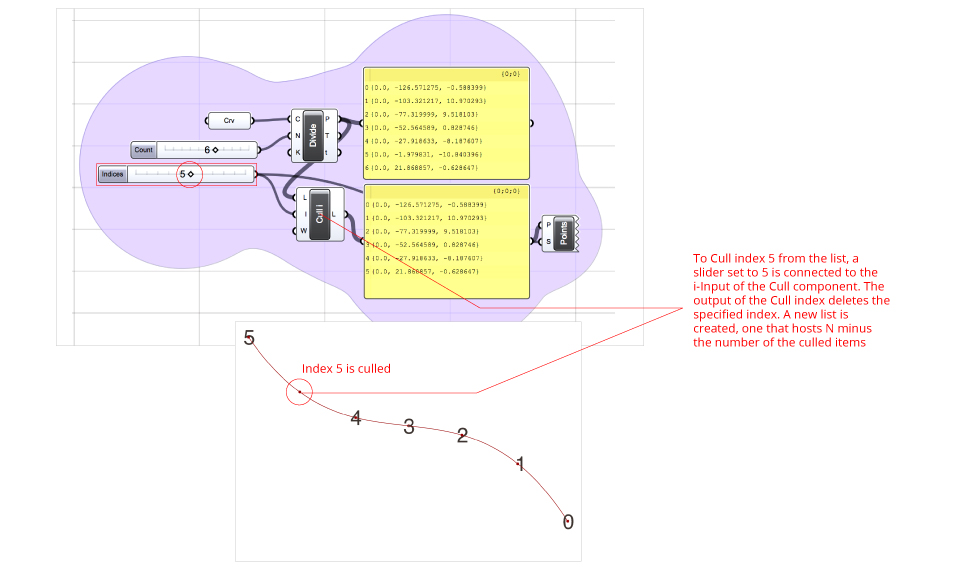
Cull Index – The Cull component deletes a specified index items from a list.
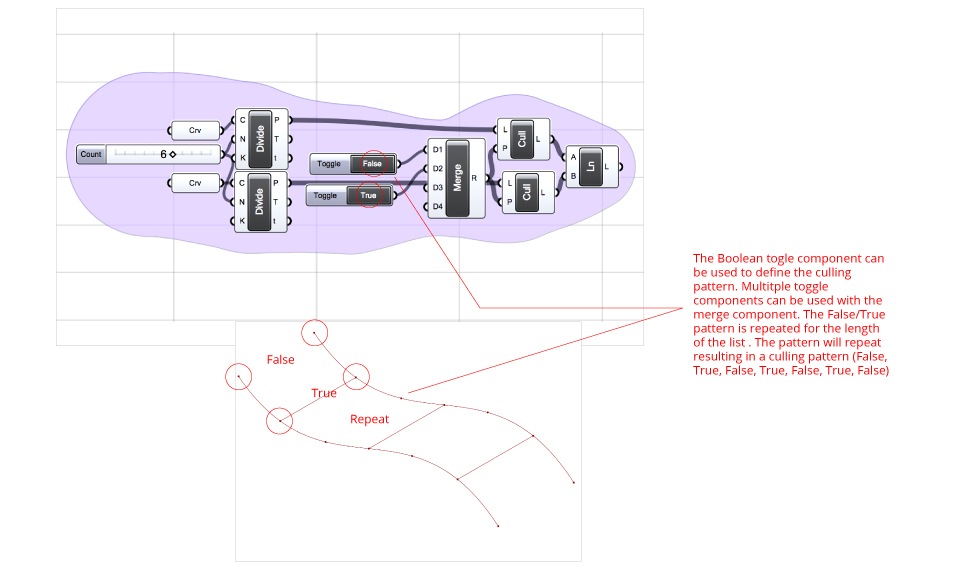
Cull Patten – Using repeating boolean values of true and false can be used to select and exclude items from a list. Cull Pattern component is used to to filter lists according to a repeating pattern of boolean values.
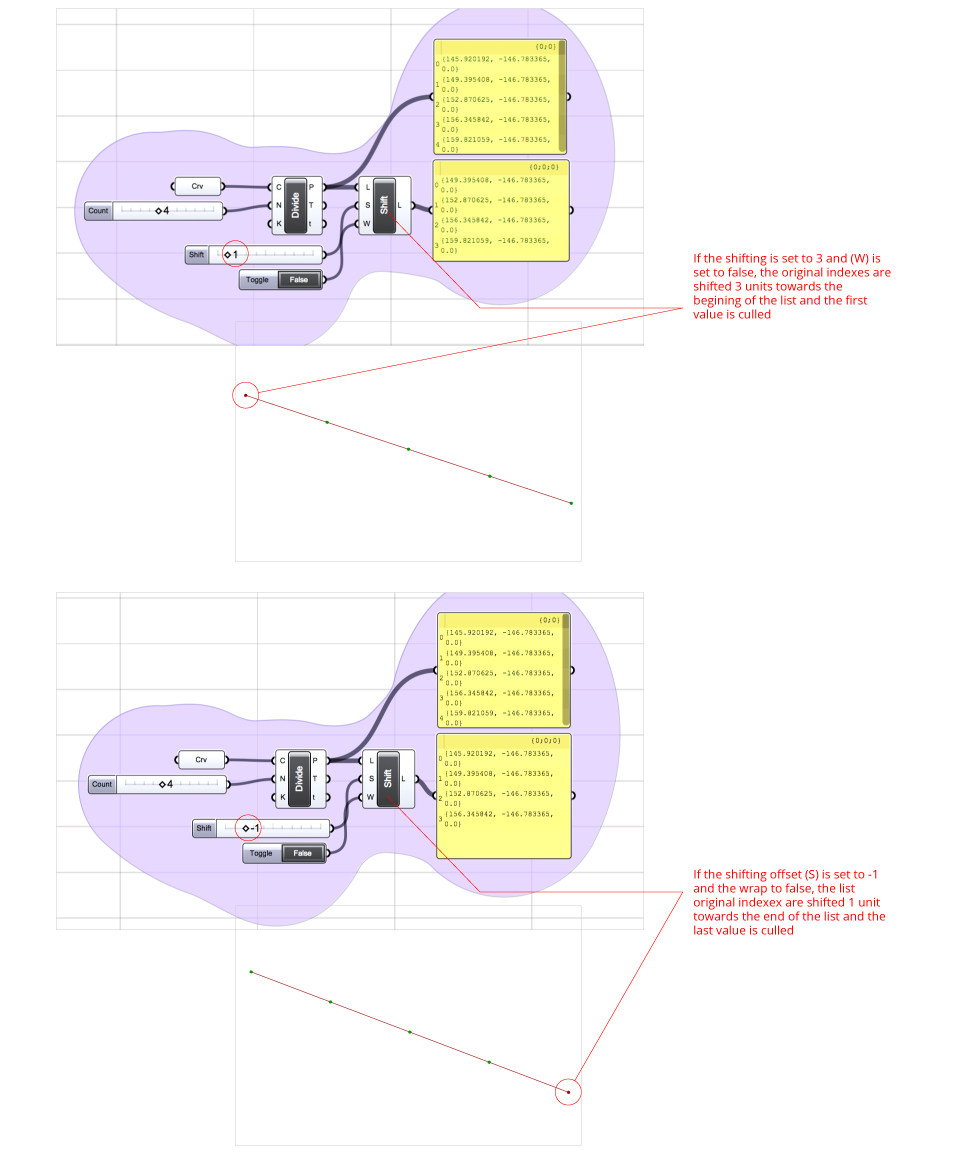
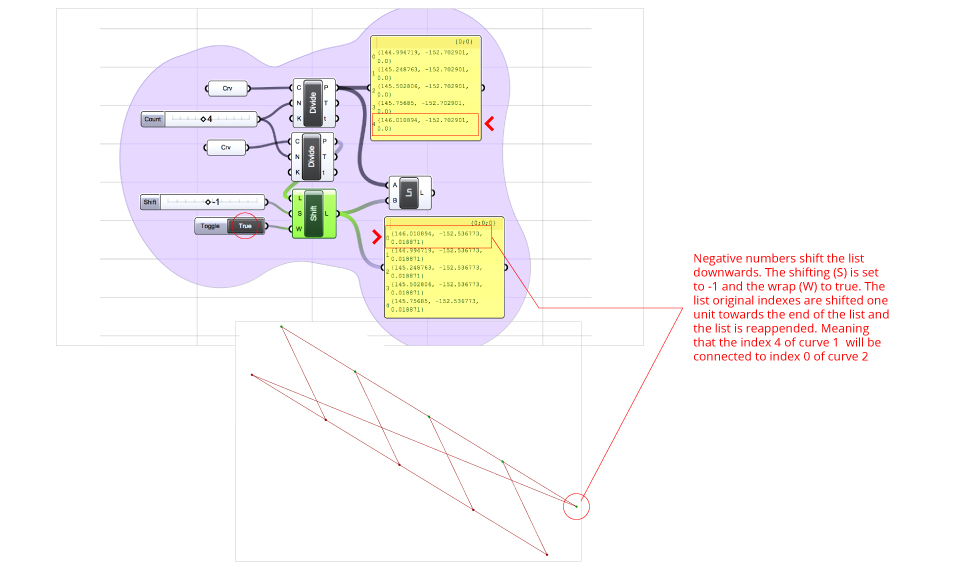
Shift List – Shifts index numbers, upwards and downwards. S-input is the shifting offset, the L-input is the list to shift, and the W-input is a boolean parameter which declares if the resulting shifting should be re-appended.
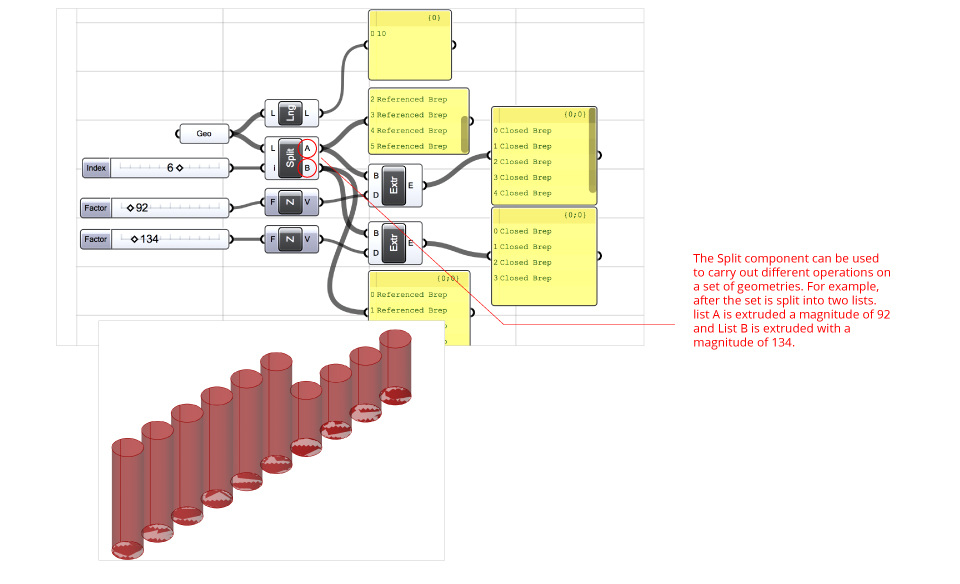
Split List – Splits a single input list at a specific index into two list A and B. List Length would let you access the length of the list if you plug it to a Panel
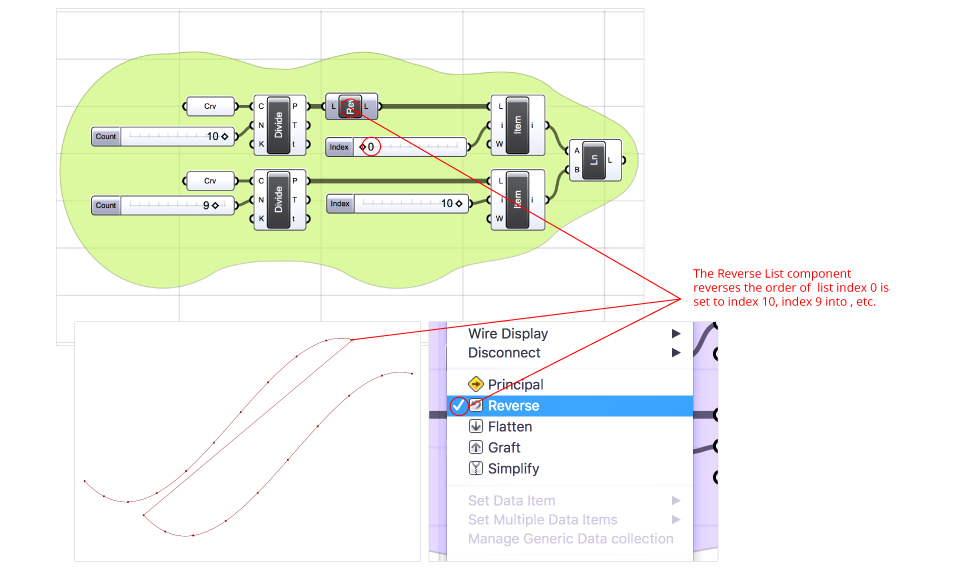
Reverse List – The Reverse List component reverses the order of the list. Index 0 is set to index 10, index 9 into 1 , etc. Every input slot embeds the functionality to reverse input data by right-clicking the slot and choosing Reverse from contextual menu.